Deciphering Digital Type: Mastering Web Page Font Size
Ever squinted at a website, struggling to decipher minuscule text? Or perhaps felt overwhelmed by giant, screen-hogging letters? Controlling web page font size is more than just a comfort feature; it’s crucial for accessibility and a positive user experience. This deep dive explores the nuances of modifying text size online, empowering you to tailor your digital reading experience.
Modifying webpage text size is a fundamental aspect of web accessibility. It allows users to personalize their browsing experience to suit their individual visual needs and preferences. From the visually impaired to those simply preferring larger or smaller text, the ability to control font size is a key element of a user-friendly web.
The history of adjustable font sizes is intertwined with the evolution of the web itself. Early web pages offered limited control over text size. As the internet matured and accessibility became a more prominent concern, browsers began incorporating features allowing users to modify font size. The rise of CSS further solidified the importance of adjustable text, offering developers more granular control over typography.
The ability to change font size is paramount for web accessibility. Individuals with visual impairments, such as low vision or dyslexia, rely on this feature to make online content readable. Furthermore, users with different screen sizes and resolutions benefit from the ability to adjust text size for optimal viewing comfort.
Failing to provide adequate control over font size can lead to several issues. Inaccessible websites exclude a significant portion of the online population. Poor readability can lead to user frustration, increased bounce rates, and a negative perception of the website. Ignoring font size control ultimately compromises the overall user experience.
Modifying text size is typically achieved through browser settings or website-specific controls. Browsers often offer zoom functionality and options to increase or decrease the default font size. Some websites provide dedicated controls, allowing users to choose from preset font sizes or use a slider for more precise adjustments.
Benefits of Adjusting Webpage Font Size:
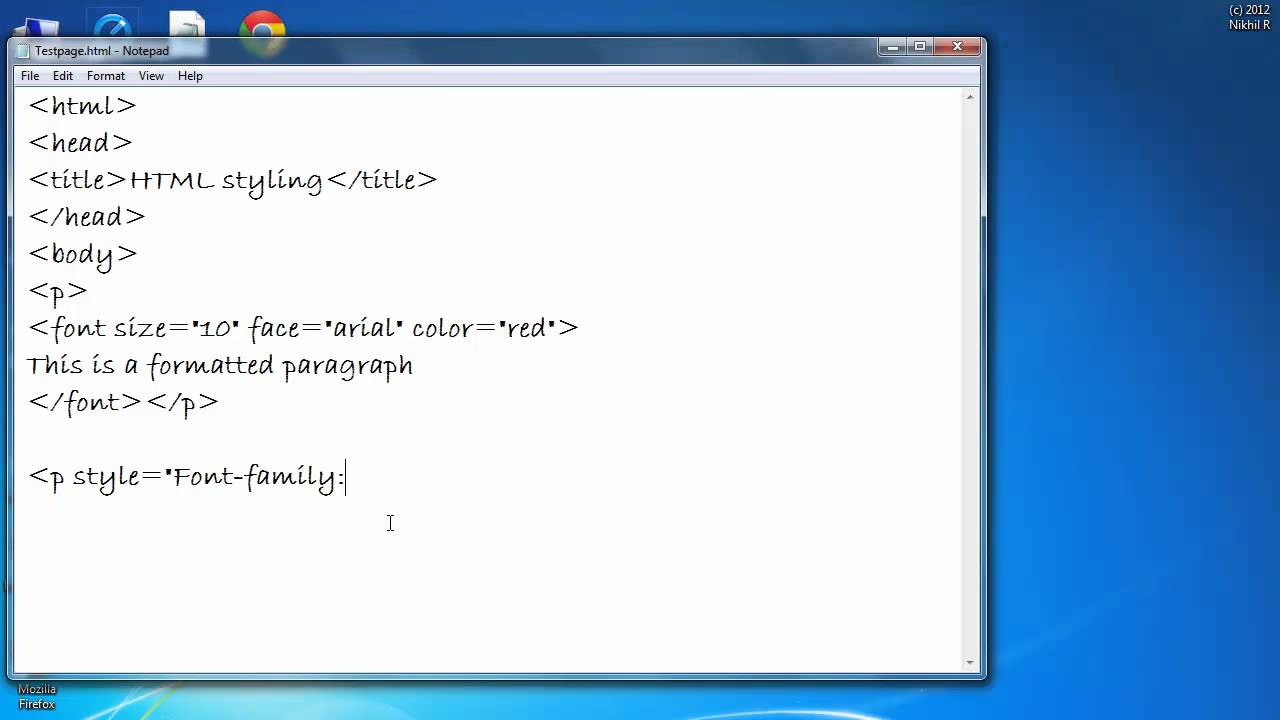
1. Enhanced Accessibility: Adjustable font size makes websites accessible to users with visual impairments, enabling them to participate fully in the online world. For example, a user with low vision can enlarge the text to a comfortable reading size.
2. Improved Readability: Users can customize text size to match their preferences and screen resolution, leading to a more comfortable and enjoyable reading experience. Someone using a small mobile screen might prefer larger text for easier reading.
3. Greater User Control: Empowering users to control font size enhances their sense of agency and personalization, creating a more positive user experience. A user with a large monitor might prefer smaller text to fit more content on the screen.
Action Plan for Implementing Adjustable Font Size:
1. Utilize relative units like 'em' or 'rem' in CSS for font sizing. This allows text to scale proportionally based on the user's default font size.
2. Test your website's readability across different font sizes and devices.
3. Provide clear instructions to users on how to adjust font size within their browser settings.
Advantages and Disadvantages of Adjustable Font Size
| Advantages | Disadvantages |
|---|---|
| Improved Accessibility | Potential layout issues if not implemented correctly |
| Enhanced Readability | May require user intervention if default sizes are not optimal |
| Increased User Satisfaction |
Best Practices:
1. Use relative font sizes.
2. Avoid fixed pixel sizes.
3. Test across various browsers and devices.
4. Provide user instructions.
5. Consider user preferences.
FAQs:
1. How do I change font size in my browser? (Answer: Refer to browser settings)
2. Why can't I change the font size on some websites? (Answer: Site might use fixed pixel sizes)
3. What are relative font sizes? (Answer: Units like 'em' and 'rem')
4. What is the best font size for web accessibility? (Answer: Depends on user preference)
5. How can I make my website more accessible? (Answer: Use relative units, provide user controls)
6. What are the common issues with implementing adjustable font sizes? (Answer: Layout issues, inconsistent rendering across browsers)
7. How do I test my website for font size accessibility? (Answer: Use different browsers, screen readers, and zoom levels)
8. What are the WCAG guidelines for font size? (Answer: WCAG Success Criterion 1.4.4: Resize text)
Tips and Tricks: Regularly test your website's readability across various font sizes. Stay updated on accessibility guidelines. Solicit user feedback on font size preferences.
In conclusion, adjusting web page font size is not merely a design choice; it's a crucial component of building an inclusive and user-friendly online experience. From enhancing accessibility for visually impaired users to improving readability for everyone, controlling text size empowers individuals to tailor their digital interactions. By understanding the history, benefits, best practices, and potential challenges, web developers and users alike can contribute to a more accessible and enjoyable web. Embracing these principles ensures that online content remains readable, accessible, and engaging for all. Take the time to optimize your website's font size and empower your users to customize their reading experience. By prioritizing accessibility and readability, you can create a more inclusive and user-friendly online environment.
The devastating impact of the wall street crash
Unleashing dreams the power of a doctor costume for girls disfraz de doctora para nina
Snoopy dice feliz noche a whimsical journey into nightly rituals