Safe Steps: Navigating Residential Handrail Height Regulations
Ever tripped on the stairs? It's a surprisingly common occurrence, and one that highlights the importance of secure and properly installed handrails. But did you know there are specific regulations governing the height of these essential safety features? Understanding residential handrail height requirements isn't just about passing inspections; it's about creating a safe and accessible environment for everyone in your home.
Navigating the world of building codes can feel daunting, especially when dealing with seemingly small details like handrail height. However, these regulations are rooted in years of research and practical experience, designed to minimize the risk of falls and injuries. This comprehensive guide will walk you through the intricacies of residential handrail height regulations, offering practical advice and insights to help you ensure your home is both beautiful and safe.
The history of handrail height regulations is intertwined with the broader evolution of building codes, which emerged from the need to standardize construction practices and ensure public safety. Early building regulations often focused on fire safety and structural integrity, but over time, the scope expanded to include accessibility and fall prevention. As our understanding of human factors and ergonomics improved, so too did the specificity of handrail height requirements, reflecting the optimal height for providing support and balance on stairways.
The primary concern addressed by handrail height regulations is, of course, preventing falls. Stairs present a significant fall hazard, particularly for children, the elderly, and people with mobility impairments. A handrail at the correct height provides a crucial point of contact, allowing individuals to maintain their balance and safely navigate the stairs. Incorrect handrail heights can actually increase the risk of falls by providing inadequate support or forcing users into awkward postures.
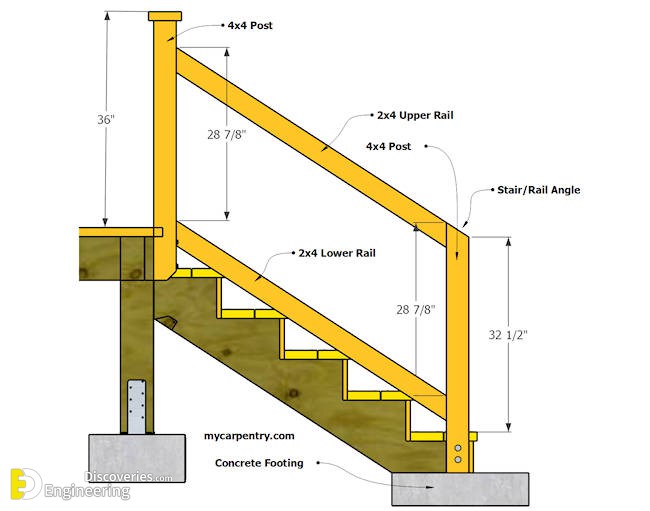
Handrail regulations establish a range of acceptable heights, usually measured vertically from the nosing of the stair tread to the top of the handrail. While specific requirements may vary slightly depending on local building codes, most jurisdictions adhere to a range of 34 to 38 inches. This standardized handrail height accommodates the average adult reach and provides comfortable support for ascending and descending stairs.
One of the primary benefits of adhering to residential handrail height regulations is enhanced safety for all occupants and visitors. Properly installed handrails significantly reduce the risk of falls, especially on staircases.
Another advantage is improved accessibility. Consistent handrail heights make navigating stairs easier for people of all ages and abilities, including children, the elderly, and individuals with mobility impairments.
Finally, complying with these regulations ensures your home meets building code requirements, avoiding potential issues during inspections or renovations.
Advantages and Disadvantages of Standardized Handrail Heights
| Advantages | Disadvantages |
|---|---|
| Increased safety | May not be ideal for extremely tall or short individuals |
| Improved accessibility | Can require adjustments during renovations or in older homes |
| Code compliance | Slight variations in local codes can cause confusion |
Best Practices for Handrail Installation
1. Consult your local building codes for specific handrail height requirements in your area.
2. Use accurate measuring tools to ensure precise handrail placement.
3. Choose sturdy and durable handrail materials that can withstand regular use.
4. Ensure handrails are securely fastened to the wall or supporting structure.
5. Provide continuous handrails along the entire length of the staircase.
Frequently Asked Questions
1. What is the standard residential handrail height? Generally, between 34 and 38 inches.
2. Do I need a handrail on both sides of the stairs? Most building codes require handrails on both sides for stairs wider than a certain measurement.
3. What materials can be used for handrails? Wood, metal, and composite materials are common choices.
4. Can I install a handrail myself? While DIY installation is possible, it's important to ensure compliance with local codes.
5. Where can I find my local building codes? Contact your local building department or municipality.
6. What happens if my handrail doesn't meet code requirements? You may be required to make adjustments to bring it into compliance.
7. Are there exceptions to handrail height requirements? Certain circumstances, such as limited space, may allow for variations with proper documentation and approvals.
8. How often should handrails be inspected? Regularly inspect handrails for damage or looseness and address any issues promptly.
Tips and Tricks for Handrail Installation: Consider using a level to ensure your handrail is perfectly horizontal. Pre-drilling pilot holes can make installation easier and prevent splitting the wood. If you're unsure about any aspect of handrail installation, consulting a qualified contractor is always a good idea.
In conclusion, understanding and adhering to residential handrail height regulations is paramount for creating a safe and accessible home. While the details of building codes can sometimes seem complex, the core principle remains simple: prioritizing the well-being of everyone who uses your stairs. By taking the time to research and implement proper handrail installations, you not only enhance the safety of your home but also contribute to a more inclusive and accessible environment for all. Don't underestimate the importance of this seemingly small detail – it can make a world of difference in preventing falls and ensuring the comfort and security of your loved ones and guests. Take the steps to ensure your home is both beautiful and safe by prioritizing proper handrail installation.
Ncaa basketball picks cbs sports insights and analysis
Lee joo bin drama list your guide to captivating performances
Unlock your inner music critic mastering song ratings