Sun-Kissed Gardens: A Guide to Thriving Vegetables in South Florida
Imagine stepping into your backyard and harvesting fresh, vibrant vegetables bathed in the warm South Florida sun. This dream can easily become a reality with a little know-how about which crops flourish in our subtropical paradise. Growing your own food offers a rewarding experience, connecting you with nature and providing healthy, delicious additions to your table. So, let's delve into the world of South Florida gardening and unlock the secrets to a bountiful harvest.
South Florida's climate, characterized by hot, humid summers and mild winters, presents unique opportunities and challenges for vegetable gardeners. While many traditional gardening practices apply, understanding the specific needs of vegetables suitable for South Florida is crucial. Selecting the right varieties and adapting your approach to the local conditions will significantly impact your garden's success.
Historically, South Florida's indigenous people cultivated a variety of crops adapted to the region's climate. These included root vegetables like cassava and boniato, along with beans, squash, and other heat-tolerant plants. Today, the tradition of gardening continues, embracing both traditional crops and a wide range of vegetables that thrive in our subtropical environment. The importance of local gardening extends beyond personal enjoyment, promoting sustainability and reducing reliance on commercially grown produce.
One of the main issues gardeners face in South Florida is the intense summer heat. Many vegetables struggle in scorching temperatures and require careful attention to watering and shading. Another challenge is the prevalence of pests and diseases, which flourish in the warm, humid conditions. Selecting disease-resistant varieties and implementing preventative measures are key to protecting your crops.
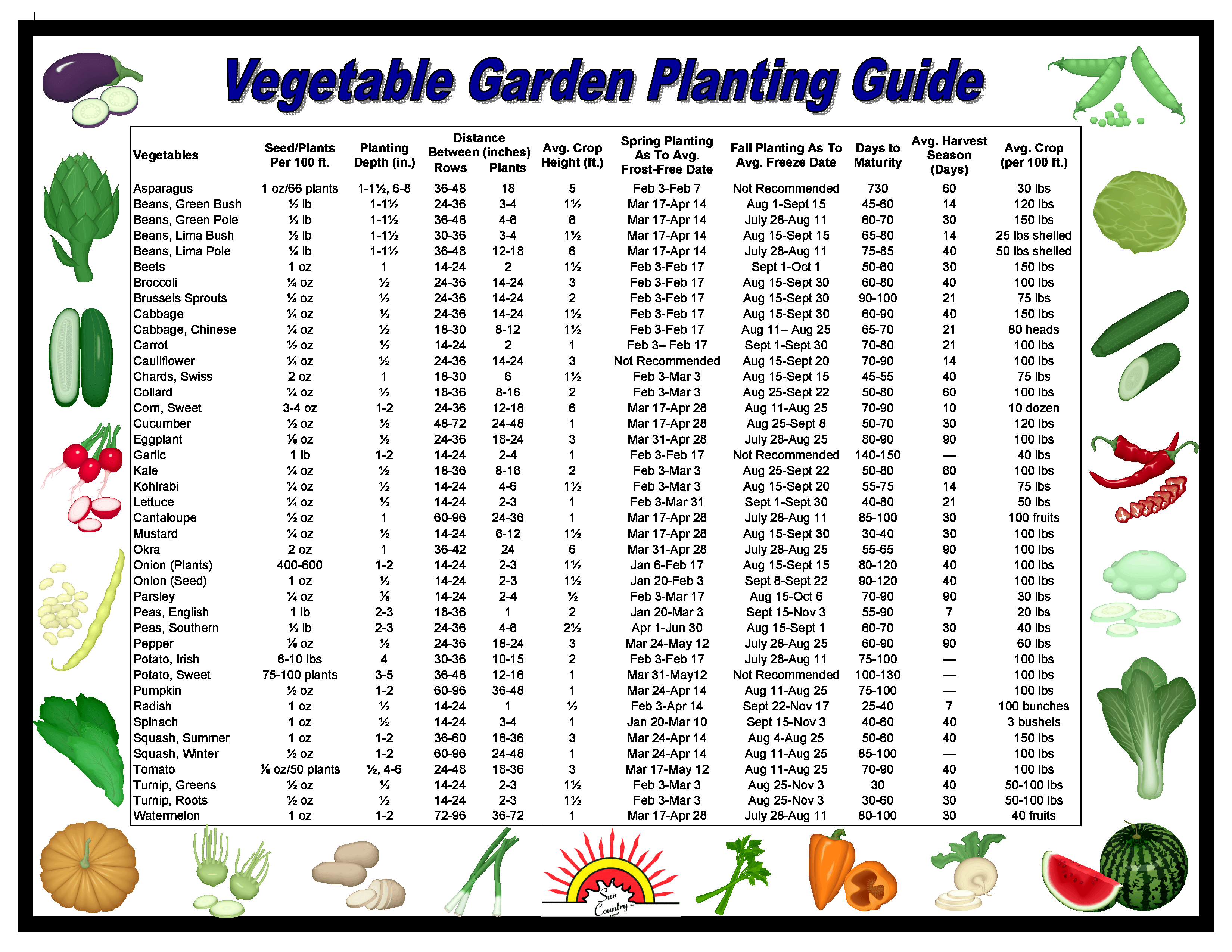
The term "suitable vegetables for South Florida" refers to plant varieties that are well-adapted to the region's unique climate and growing conditions. These plants typically tolerate heat and humidity, and some can even withstand occasional flooding or drought. Examples include tomatoes, peppers, beans, squash, okra, and leafy greens like spinach and kale (planted during the cooler months).
One benefit of gardening in South Florida is the extended growing season. Unlike colder climates with limited growing periods, you can enjoy fresh produce almost year-round. For instance, tomatoes can be grown throughout the winter months, providing a continuous supply of ripe, juicy fruits. Another advantage is the abundance of sunshine, which promotes vigorous plant growth and high yields. Furthermore, gardening provides a connection to nature and offers a therapeutic and stress-relieving activity.
Creating a successful South Florida vegetable garden involves several key steps. First, choose a sunny location with well-drained soil. Next, prepare the soil by adding compost or other organic matter to improve fertility and drainage. Then, select appropriate vegetable varieties and plant them according to their specific needs. Regular watering, fertilization, and pest control are essential for maintaining healthy plants and maximizing yields.
Advantages and Disadvantages of Growing Vegetables in South Florida
| Advantages | Disadvantages |
|---|---|
| Long growing season | Intense summer heat |
| Abundant sunshine | High humidity and pest pressure |
| Diverse variety of crops | Potential for soil-borne diseases |
Five best practices for South Florida vegetable gardening include choosing the right varieties, providing adequate water and nutrients, protecting plants from pests and diseases, utilizing shade cloth during the hottest months, and amending the soil with organic matter.
Examples of successful South Florida gardens include community gardens, rooftop gardens, and backyard plots. These gardens demonstrate the versatility and potential of urban agriculture in the region.
Challenges include pests like nematodes and solutions involve using resistant varieties. Another challenge is the intense sun and a solution is shade cloth.
FAQ: What are the best vegetables for beginners? What are the common pests? When should I plant tomatoes?
Tips and Tricks: Use mulch to retain moisture. Rotate crops to prevent disease buildup. Harvest vegetables regularly to encourage continuous production.
Cultivating a thriving vegetable garden in South Florida is a rewarding endeavor that connects you with nature and provides fresh, healthy food for your table. By understanding the unique challenges and opportunities presented by our subtropical climate and selecting appropriate vegetable varieties, you can create a bountiful oasis in your backyard. Embrace the joy of gardening and enjoy the fruits (and vegetables!) of your labor. Remember to continue learning about best practices, experiment with different crops, and connect with local gardening communities for support and inspiration. Start small, have patience, and enjoy the journey of growing your own food in beautiful South Florida.
A timeless tradition capturing the spirit of the la county fair
Unlock your childs potential 1st grade worksheet packet printable free
Decoding the air force tattoo policy your guide to ink and enlistment