Understanding the WHO's Life Course Perspective
Have you ever considered the interconnectedness of your experiences throughout life and their impact on your overall health and well-being? The World Health Organization (WHO) has, and they've developed a framework known as the life course perspective. While searching for "etapas de la vida oms pdf" might lead you to specific documents, the core idea revolves around understanding how different stages of life, from infancy to old age, influence health outcomes.
The life course perspective isn't just about categorizing individuals into age groups. It recognizes that our experiences accumulate over time, shaping our physical and mental health. This approach goes beyond simply treating illnesses and focuses on promoting health and preventing disease across the entire lifespan. Think of it as a long-term investment in well-being, starting even before birth.
The origins of the life course perspective can be traced back to various disciplines, including epidemiology, sociology, and developmental psychology. Researchers observed that early life experiences, such as childhood adversity or access to quality education, could have profound and lasting effects on health later in life. This realization led to a shift in how we think about health, moving from a reactive approach to a more proactive and preventative one.
The WHO's adoption of the life course perspective is crucial for several reasons. It provides a framework for understanding the complex interplay of biological, social, and environmental factors that influence health throughout life. This understanding is essential for developing effective public health interventions that address the root causes of disease and promote overall well-being. Furthermore, the life course approach emphasizes the importance of equity and social justice, recognizing that not everyone has the same opportunities for a healthy life.
One of the key implications of the life course perspective is the need for integrated and coordinated health services across the lifespan. This means moving away from fragmented care and towards a more holistic approach that considers the individual's entire life history. By addressing the social determinants of health, such as poverty, education, and access to healthcare, we can create healthier societies for everyone.
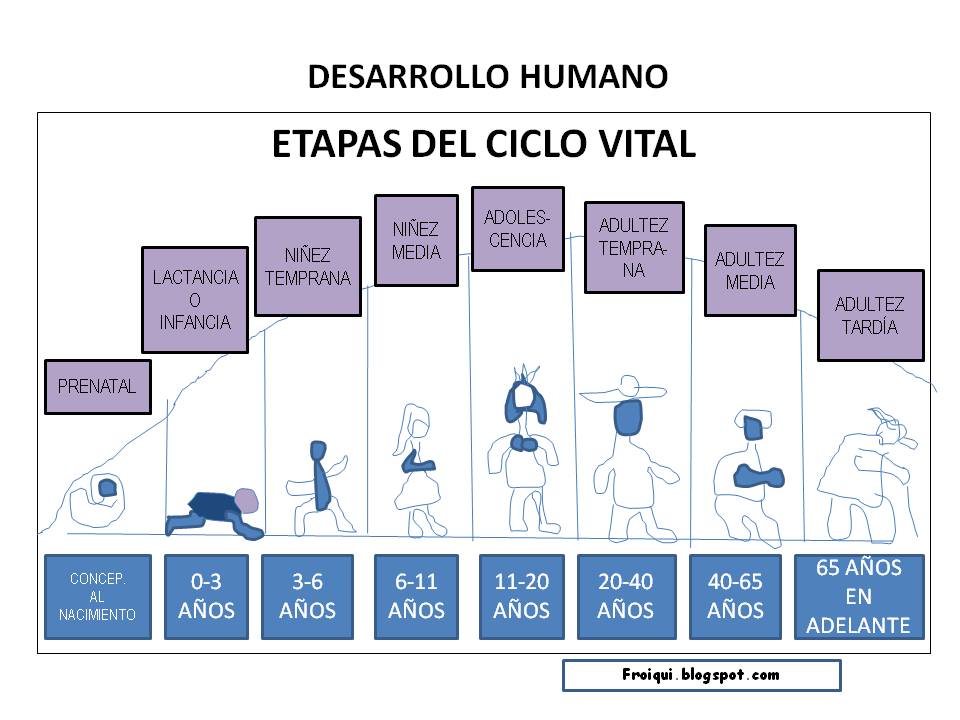
The WHO's life course approach emphasizes several key life stages, including pregnancy and early childhood, adolescence, adulthood, and older age. Each stage presents unique opportunities and challenges for health and development. For instance, ensuring adequate nutrition during pregnancy can have a significant impact on the child's health throughout their life. Similarly, promoting healthy behaviors during adolescence can help prevent chronic diseases later in life.
Understanding the life course perspective offers several benefits. It allows for early interventions to prevent future health problems, promotes a more holistic approach to healthcare, and empowers individuals to take control of their own health throughout their lives. By recognizing the interconnectedness of experiences across the lifespan, we can create healthier and more equitable societies.
While there isn't a specific "etapas de la vida oms pdf" checklist or step-by-step guide, the core principles of the life course approach encourage proactive engagement with health throughout life. This includes making healthy lifestyle choices, seeking preventative care, and advocating for policies that support health and well-being across all life stages.
Advantages and Disadvantages of the Life Course Perspective
| Advantages | Disadvantages |
|---|---|
| Holistic Approach | Complexity of Implementation |
| Preventive Focus | Data Collection Challenges |
| Promotes Health Equity | Long-Term Investment Required |
FAQs:
1. What is the life course perspective? (A framework for understanding how experiences throughout life impact health.)
2. Why is it important? (It promotes a proactive and preventative approach to health.)
3. What are the key life stages? (Pregnancy, childhood, adolescence, adulthood, older age.)
4. How can I apply this to my own life? (Make healthy choices and seek preventative care.)
5. What are the social determinants of health? (Factors like poverty, education, and access to care.)
6. How does this approach benefit society? (Creates healthier and more equitable communities.)
7. Where can I learn more? (Consult WHO resources and public health journals.)
8. What are some challenges in implementing this approach? (Resource limitations and data collection complexities.)
In conclusion, the WHO's life course perspective offers a powerful framework for understanding and improving health across the lifespan. It emphasizes the interconnectedness of experiences, promotes a proactive approach to health, and highlights the importance of addressing the social determinants of health. While a specific "etapas de la vida oms pdf" might provide further details, the core principles encourage us to view health as a lifelong journey, not just a destination. By embracing this perspective, we can empower individuals, communities, and policymakers to create a healthier and more equitable future for all. This requires ongoing learning, advocating for supportive policies, and engaging in healthy practices throughout our lives. The life course approach is not just a theory; it's a call to action for a healthier future.
Easy toe nail designs for a chic look
Elevate your digital domain discovering the allure of cool background wallpapers for your computer gif included
Furnace drain sos prevent a flood with this diy guide