Unlocking AC Circuit Secrets: Mastering Phasor Diagrams for Inductors and Capacitors
Ever feel like AC circuit analysis is a tangled mess of sines and cosines? Trying to keep track of voltage and current relationships in circuits with inductors and capacitors can feel like juggling chainsaws. But there's a secret weapon that can bring order to this chaos: the phasor diagram. This visual tool simplifies complex AC circuit analysis, allowing you to see the interplay between voltage and current in a whole new light.
Phasor diagrams represent sinusoidal voltages and currents as rotating vectors, or "phasors." These phasors rotate counterclockwise at the angular frequency of the AC source. Their length corresponds to the magnitude of the voltage or current, and their angle represents the phase shift relative to a reference phasor. This graphical representation transforms tricky trigonometric calculations into simple vector additions and subtractions, making circuit analysis much more manageable.
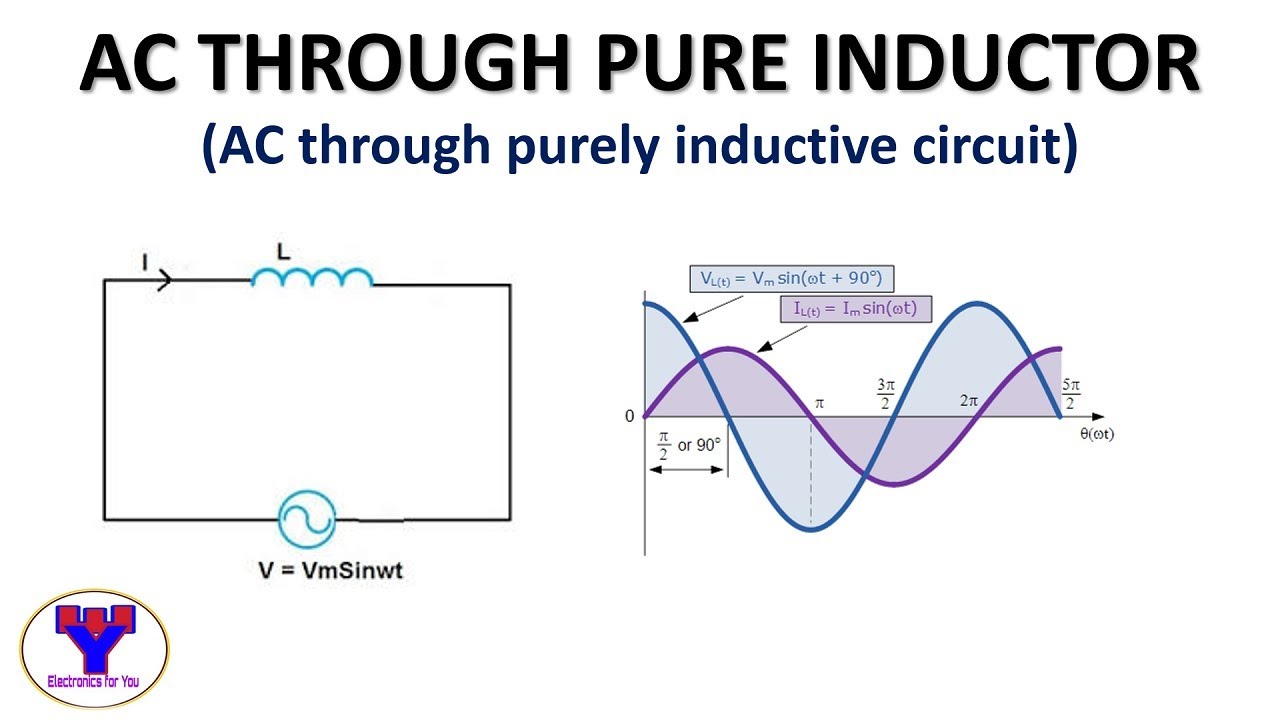
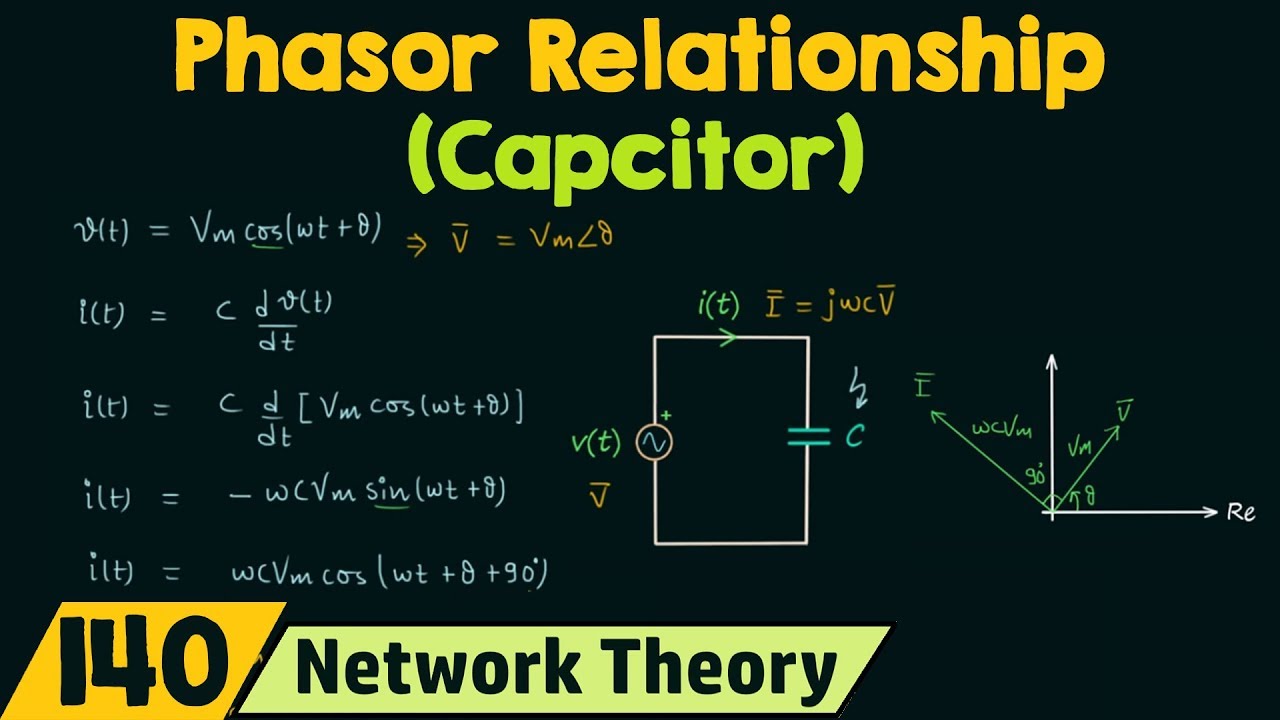
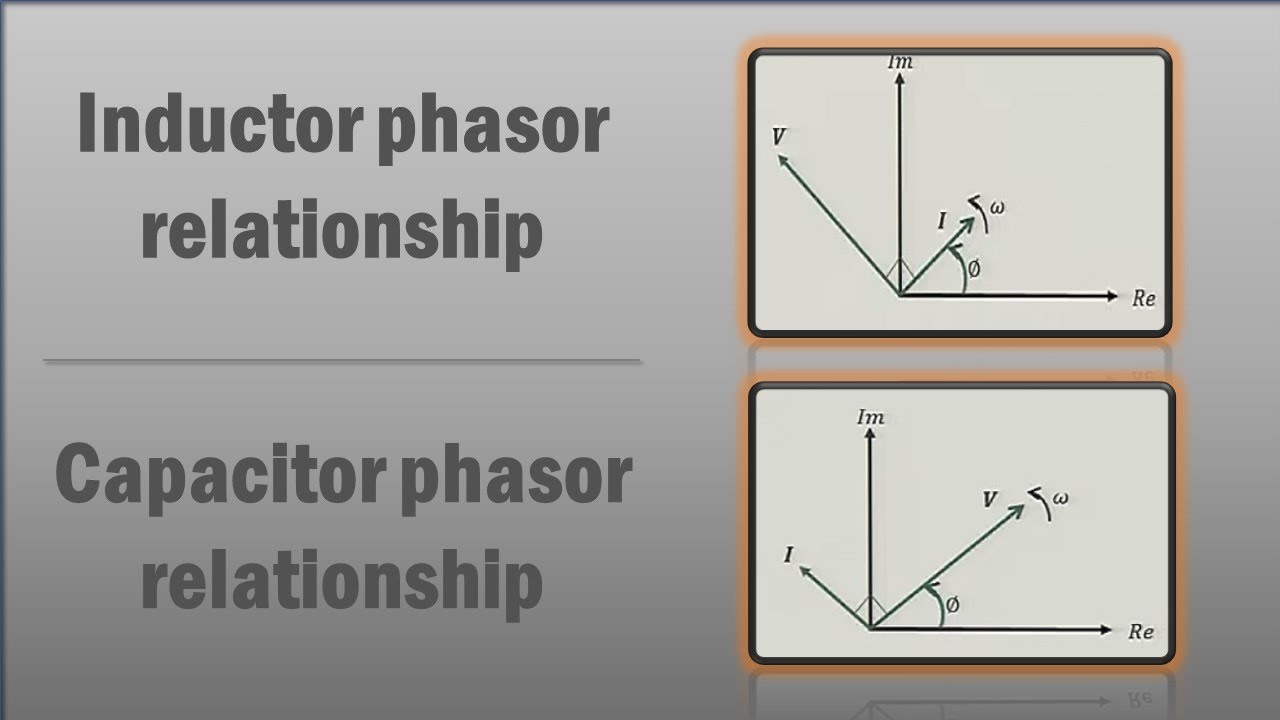
Imagine trying to visualize the current and voltage relationship in a circuit containing an inductor. You know the current lags the voltage, but by how much? A phasor diagram instantly clarifies this relationship, visually depicting the 90-degree phase difference. Similarly, for a capacitor, the phasor diagram clearly illustrates the current leading the voltage by 90 degrees. This intuitive visual representation is invaluable for understanding the behavior of AC circuits.
The concept of phasor diagrams emerged from the need to simplify complex AC circuit calculations. Early electrical engineers grappled with tedious trigonometric equations, making circuit analysis a time-consuming process. Phasor diagrams provided a much-needed shortcut, transforming complex calculations into simpler vector operations. This graphical approach revolutionized AC circuit analysis, paving the way for the design of more sophisticated electrical systems.
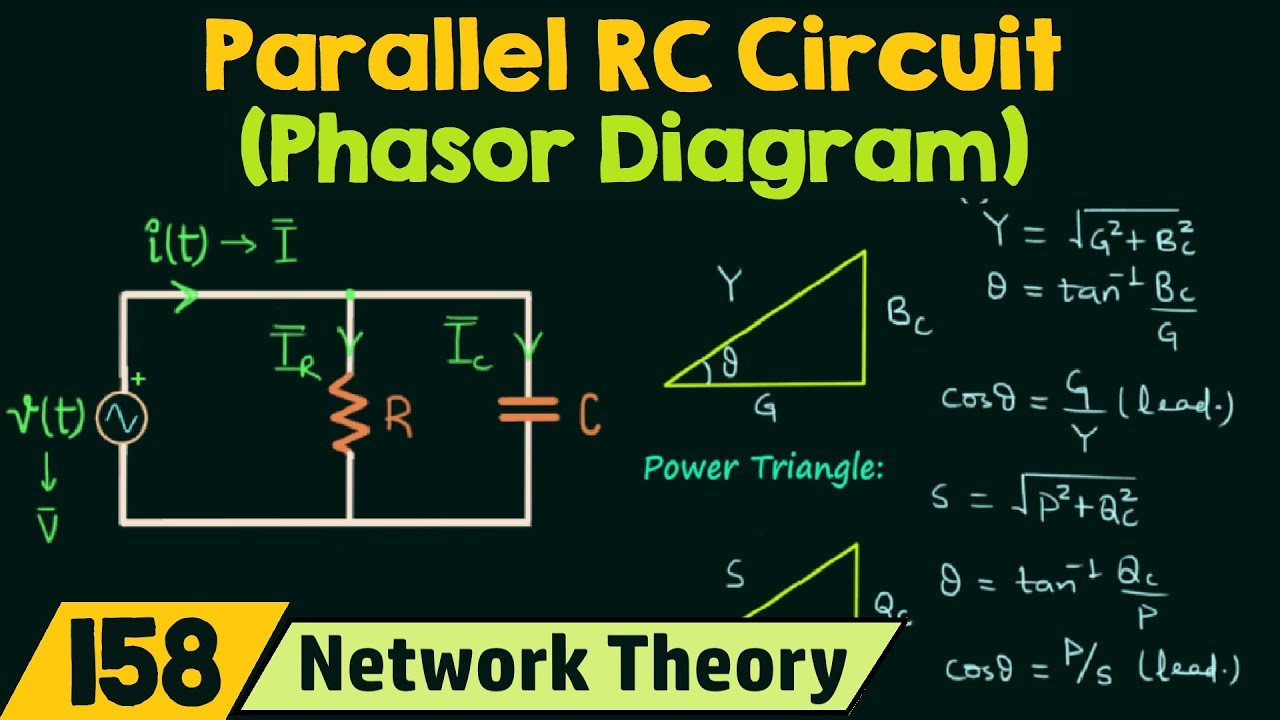
Understanding phasor diagrams is crucial for anyone working with AC circuits. From designing power grids to troubleshooting electronic devices, these diagrams provide insights into circuit behavior. One of the key challenges in AC circuit analysis involves dealing with reactance, the opposition offered by inductors and capacitors to the flow of alternating current. Phasor diagrams help visualize this opposition and its impact on the overall circuit impedance, the total opposition to current flow. By representing reactances and impedances as vectors, phasor diagrams simplify the process of calculating the total impedance of complex circuits.
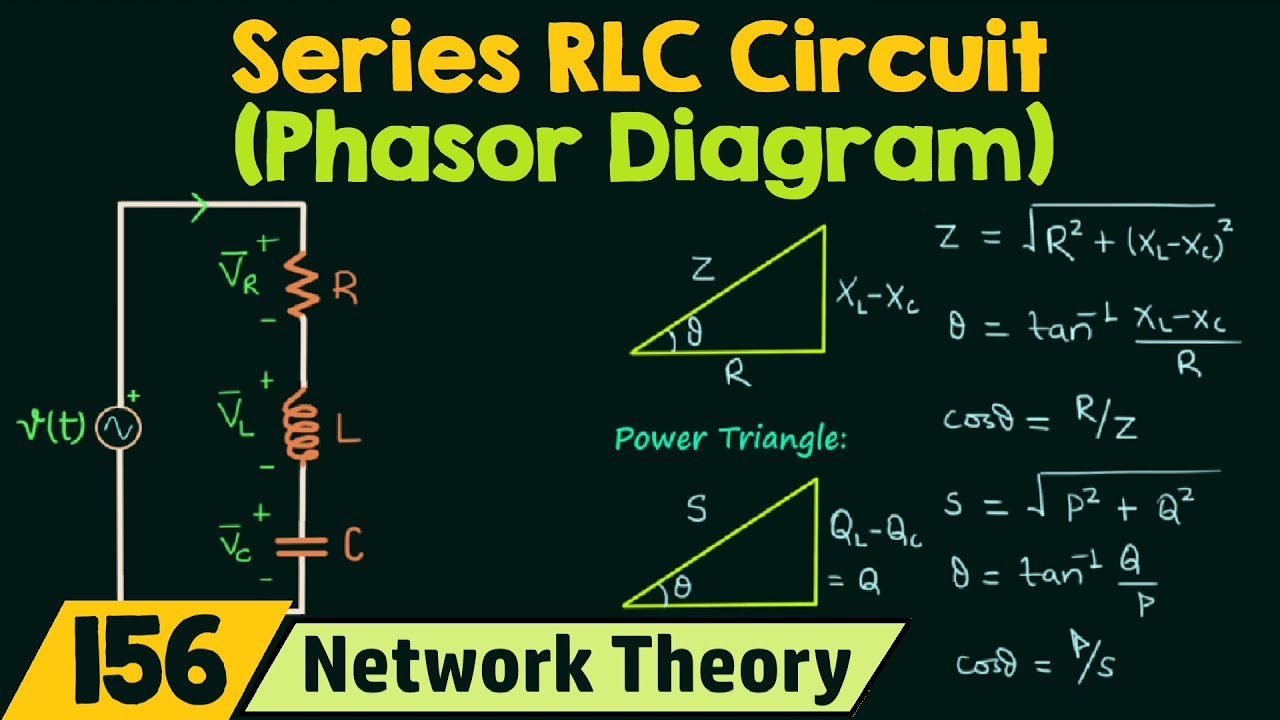
A capacitor phasor diagram shows the current phasor leading the voltage phasor by 90 degrees. An inductor phasor diagram shows the current phasor lagging the voltage phasor by 90 degrees. In a series LC circuit, the voltage across the inductor leads the current by 90 degrees, while the voltage across the capacitor lags the current by 90 degrees.
Benefits of using phasor diagrams include: simplified analysis of complex circuits, easy visualization of phase relationships, and efficient calculation of impedance. For example, in a series RLC circuit, the phasor diagram allows you to easily determine the overall impedance by vectorially adding the resistance, inductive reactance, and capacitive reactance.
To construct a phasor diagram, choose a reference phasor, typically the source voltage. Then, draw the phasors for the current and voltages across each component, taking into account their respective phase shifts. The resulting diagram provides a clear visual representation of the circuit's behavior.
Advantages and Disadvantages of Phasor Diagrams
| Advantages | Disadvantages |
|---|---|
| Simplifies complex AC circuit analysis | Only applicable to sinusoidal waveforms |
| Visualizes phase relationships | Can be complex for very large circuits |
| Facilitates impedance calculations | Doesn't represent transient behavior |
Best Practices: 1. Always choose a reference phasor. 2. Ensure accurate representation of phase shifts. 3. Use appropriate scales for magnitudes. 4. Clearly label all phasors. 5. Double-check your diagram for consistency.
FAQs: 1. What is a phasor? 2. Why do we use phasor diagrams? 3. How do I draw a phasor diagram for a series circuit? 4. How do I calculate impedance using a phasor diagram? 5. What is the difference between a phasor and a vector? 6. How do phasor diagrams help with AC circuit analysis? 7. What are the limitations of phasor diagrams? 8. Where can I learn more about phasor diagrams?
Tips and Tricks: Use different colors for voltage and current phasors. Draw the diagram to scale for better visualization. Practice drawing phasor diagrams for various circuit configurations.
In conclusion, the phasor diagram is an indispensable tool for anyone working with AC circuits. It provides a powerful visual method for simplifying complex analysis, visualizing phase relationships, and calculating impedance. Mastering phasor diagrams will significantly enhance your understanding of AC circuit behavior and empower you to tackle even the most challenging circuit problems. By utilizing the tips and best practices outlined, and by understanding the advantages and limitations of phasor diagrams, you can unlock a deeper understanding of how AC circuits operate, enabling you to design, analyze, and troubleshoot with confidence. Start practicing with phasor diagrams today and transform your approach to AC circuit analysis. Embrace this powerful technique and elevate your electrical engineering skills to the next level.
Unlock the cleaning power of baking soda
Unlocking the joy the hilarious world of the dog laughing meme
Unraveling time exploring the world of harry peverell time travel fanfiction