Unlocking Circuit Secrets: The Power of Phasor Diagrams
Ever stare at a jumbled mess of resistors, inductors, and capacitors and feel utterly lost? Like trying to decipher hieroglyphics? That's the feeling many encounter when dealing with alternating current (AC) circuits. Luckily, there's a secret weapon: the phasor diagram. Imagine trying to juggle three balls while riding a unicycle – sounds complicated, right? Well, AC circuits with their fluctuating voltages and currents can feel just as tricky. But phasor diagrams are our unicycle, providing the stability and perspective needed to navigate this complex world.
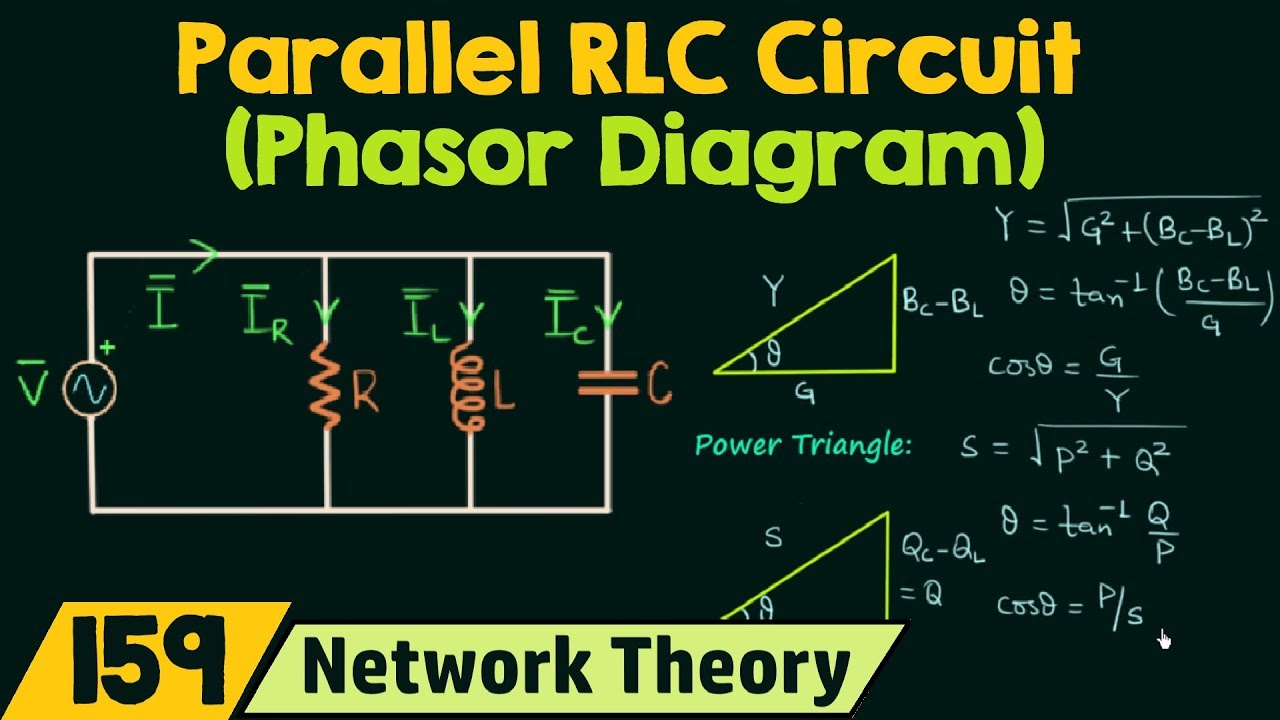
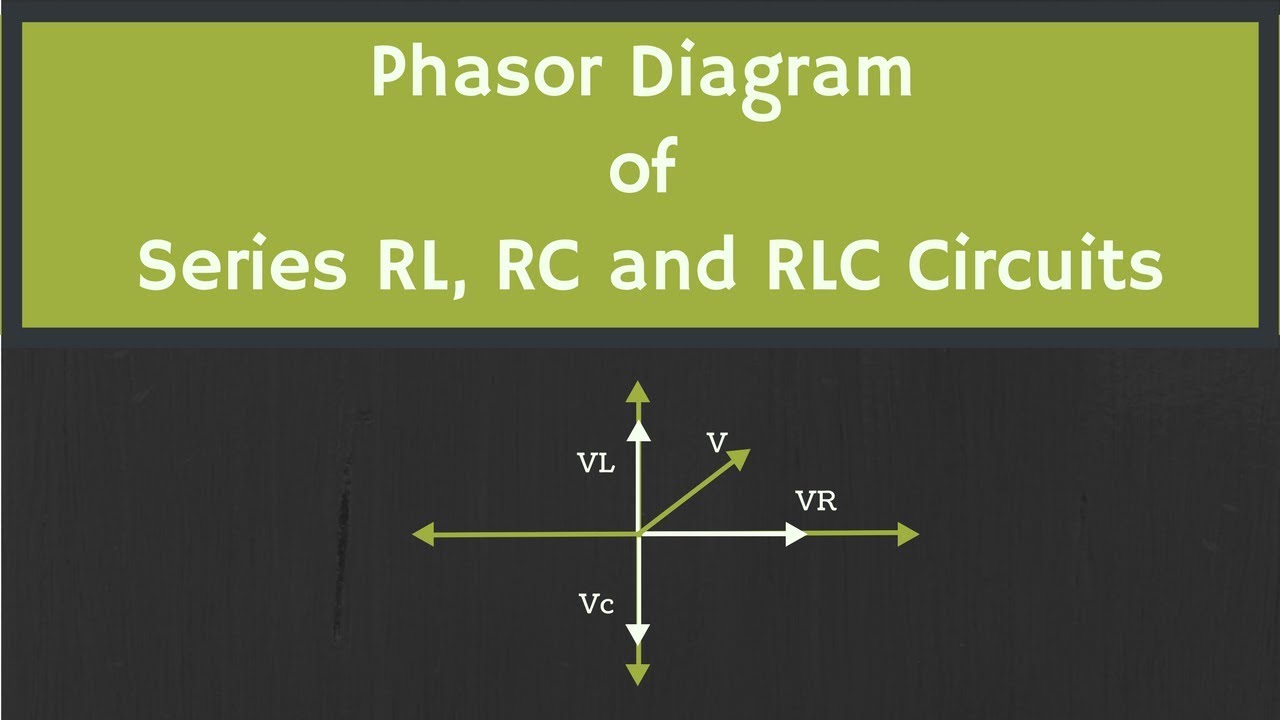
So, what exactly *is* a phasor diagram for an RLC circuit? It's a visual representation, a snapshot in time, of the relationship between voltage and current in a circuit containing resistors (R), inductors (L), and capacitors (C). Instead of grappling with constantly changing sine waves, we use rotating vectors, called phasors, to represent these quantities. The length of the phasor corresponds to the magnitude, and the angle represents the phase difference between voltage and current. This simple yet ingenious tool transforms complex calculations into understandable geometric relationships.
The concept of phasors stems from the work of Charles Proteus Steinmetz, a brilliant mathematician and electrical engineer, in the late 19th century. As AC systems became increasingly prevalent, the need for a simpler method of analyzing these circuits became apparent. Steinmetz's introduction of phasor diagrams revolutionized circuit analysis, providing a powerful tool for engineers and scientists. Without this graphical approach, understanding and designing AC circuits, which power everything from our homes to industrial machinery, would be significantly more challenging.
A crucial aspect of using phasor diagrams is understanding impedance. Impedance represents the total opposition to current flow in an AC circuit, incorporating resistance, inductive reactance, and capacitive reactance. These reactances arise from the energy storage properties of inductors and capacitors, affecting how they respond to changes in voltage and current. Phasor diagrams elegantly illustrate the relationship between these components of impedance, enabling us to calculate the overall circuit behavior and predict its response to varying frequencies.
One of the main challenges related to phasor diagrams is visualizing the rotating vectors and their relationships. It requires a shift in perspective from the time domain, where we see waveforms changing over time, to the frequency domain, where we focus on the magnitude and phase of these waveforms. However, once mastered, this perspective shift unlocks a powerful tool for understanding circuit behavior. It’s like switching from a close-up view of individual ants to a wider perspective of the entire ant colony, providing a much clearer understanding of the overall system.
A simple example is a series RLC circuit. The resistor's voltage and current are in phase, represented by a phasor along the horizontal axis. The inductor's voltage leads the current by 90 degrees, while the capacitor's voltage lags the current by 90 degrees. By drawing these phasors, we can easily determine the total impedance and the phase difference between the source voltage and current.
Benefits of Phasor Diagrams: 1. Simplified Analysis: Converting sinusoidal functions into phasors simplifies calculations. 2. Visualization: Phasors offer a visual representation of circuit behavior. 3. Impedance Analysis: Phasor diagrams allow for easy determination of impedance and phase relationships.
Creating a phasor diagram: 1. Identify the frequency of the AC source. 2. Calculate the impedance of each component. 3. Draw the phasors for each component's voltage or current. 4. Combine the phasors to determine the overall circuit behavior.
Advantages and Disadvantages of Phasor Diagrams
| Advantages | Disadvantages |
|---|---|
| Simplified calculations | Requires understanding of complex numbers |
| Visual representation of circuit behavior | Limited to steady-state analysis |
| Easy determination of impedance | Can be challenging for complex circuits |
FAQ: What is a phasor? What is impedance? How do I draw a phasor diagram? What is the difference between resistance and reactance? How do I calculate impedance in a series RLC circuit? How do I calculate impedance in a parallel RLC circuit? What is resonance in an RLC circuit? How can I use a phasor diagram to analyze resonance?
Tips and Tricks: Practice drawing phasor diagrams for different circuit configurations. Use software tools to simulate and visualize phasor diagrams. Relate phasor diagrams to the physical behavior of the circuit components.
In conclusion, phasor diagrams are an invaluable tool for anyone working with AC circuits. They provide a powerful and intuitive way to understand complex circuit behavior, simplify calculations, and visualize the relationships between voltage, current, and impedance. From designing efficient power systems to troubleshooting electronic devices, mastering phasor diagrams unlocks a deeper understanding of the electrical world around us. By embracing this visual approach, we can move from feeling lost in a maze of components to confidently navigating the intricate landscape of AC circuits. Explore further by researching resources like online tutorials, textbooks on circuit analysis, and circuit simulation software. Embark on this journey, and unlock the secrets of RLC circuits through the power of phasor diagrams.
Decoding bodega aurrera mexicos retail giant
Unleash your social media power mastering posting apps
Honoring lifes journey northcutt son funeral home hillsboro ky