Unlocking Power Transmission: Your Guide to Standard Key Sizes for Shafts
Imagine a world without the seamless transfer of power – gears grinding to a halt, conveyors ceasing their rhythmic motion, and industrial processes coming to a standstill. This is the potential consequence of overlooking a seemingly small, yet critical component: the key. This often-unseen element plays a vital role in connecting shafts and hubs, ensuring the effective transmission of rotational power. Understanding standard key sizes for shafts is paramount for engineers, mechanics, and anyone involved in the design, maintenance, or operation of machinery.
Selecting the correct key size for a shaft is not merely a matter of picking a random dimension. It requires a careful consideration of factors such as shaft diameter, torque requirements, and material properties. A properly sized key ensures a secure connection, preventing slippage and potential damage to both the shaft and the hub. Conversely, an incorrectly sized key can lead to premature wear, key failure, and ultimately, system breakdown.
This comprehensive guide delves into the intricacies of keyway sizing, providing valuable insights into how to determine the appropriate key dimensions for your specific application. We'll explore the various types of keys, the relevant standards that govern their dimensions, and the factors that influence key selection. By understanding these principles, you can ensure the reliability and longevity of your machinery.
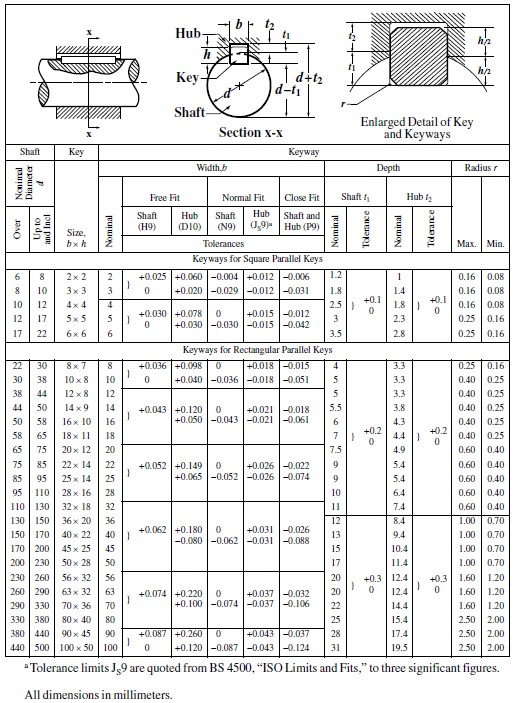
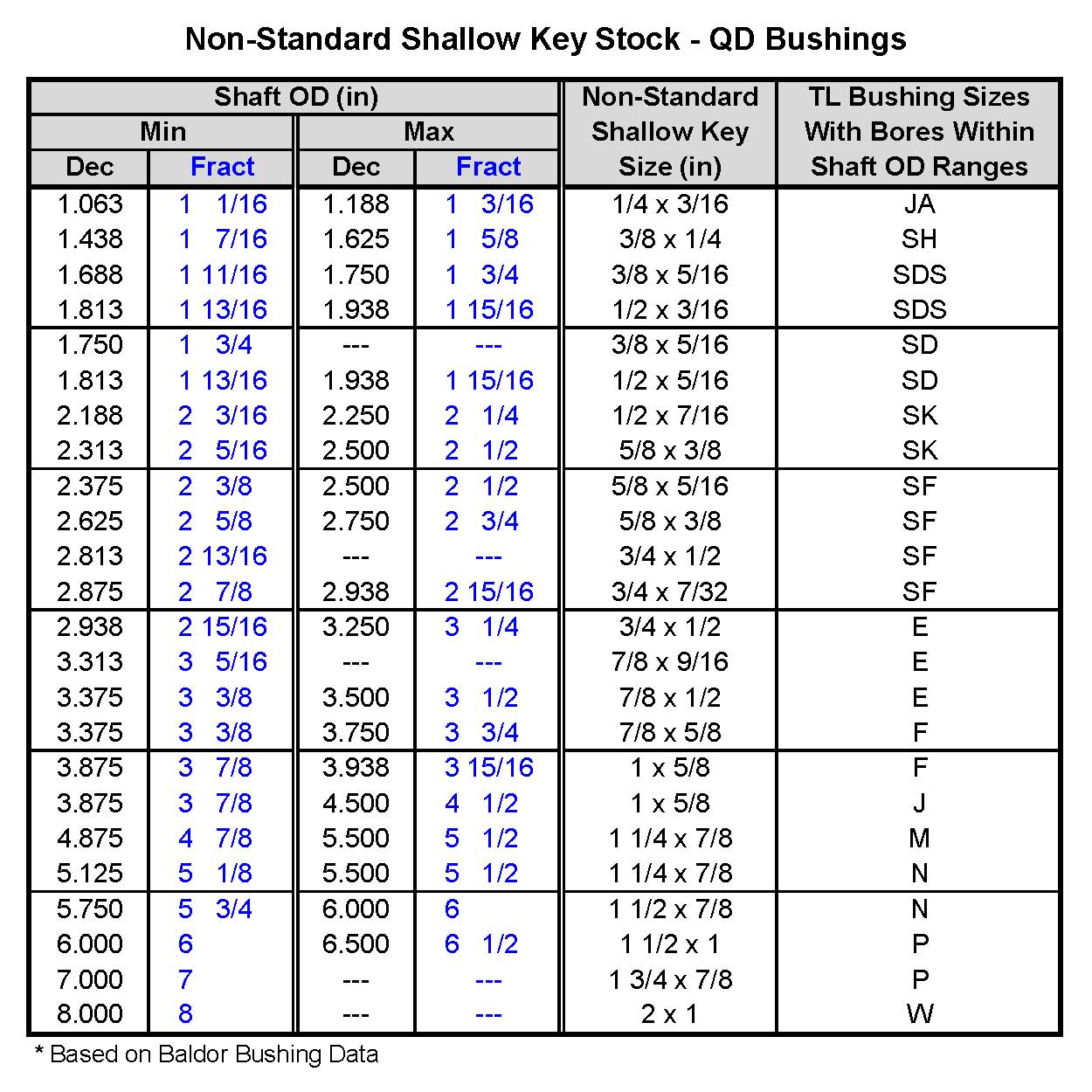
The historical development of standardized key dimensions is a testament to the ongoing quest for efficient power transmission. Over time, engineers and manufacturers recognized the need for uniformity in key sizes to simplify design, manufacturing, and maintenance processes. Standardization ensures interchangeability, reduces costs, and promotes safety. Charts and tables outlining standard key sizes for various shaft diameters have become indispensable tools for engineers and machinists.
These standardized dimensions, often codified by organizations like ANSI (American National Standards Institute) and ISO (International Organization for Standardization), offer a framework for selecting the correct key size. These standards take into account a range of factors, including material strength, operating conditions, and safety margins. Using these standards ensures compatibility and simplifies the design process.
A key's primary function is to transmit torque from a shaft to a hub (or vice versa). It achieves this by fitting snugly into keyways machined into both the shaft and the hub, creating a positive mechanical connection. This connection prevents relative rotation between the two components, ensuring efficient power transfer. For example, in a motor connected to a pump, the key ensures that the rotational power of the motor is effectively transmitted to the pump shaft.
Benefits of using standard key sizes include: 1. Interchangeability: Standard keys are readily available and can be easily replaced. 2. Cost-effectiveness: Standardization streamlines manufacturing processes, leading to lower costs. 3. Reliability: Properly sized standard keys ensure reliable power transmission, reducing the risk of failures.
Challenges in key selection can arise from factors such as high torque applications, unusual shaft sizes, or harsh operating environments. Solutions may involve using specialized key materials, custom key designs, or alternative connection methods.
Advantages and Disadvantages of Standard Keys
| Advantages | Disadvantages |
|---|---|
| Simplicity | Stress Concentration |
| Easy to manufacture | Weakening of Shaft |
| Low Cost | Limited Torque Capacity |
Best Practice: Always refer to relevant standards (e.g., ANSI, ISO) when selecting key sizes.
Best Practice: Ensure proper keyway machining tolerances for a secure fit.
Best Practice: Select appropriate key material based on the application's load and environmental conditions.
Best Practice: Inspect keys regularly for wear and tear.
Best Practice: Ensure proper installation to avoid damage to the key, shaft, and hub.
FAQ: What is a keyway? (A keyway is a slot machined into a shaft or hub to accommodate a key.)
FAQ: What are the different types of keys? (Common types include square keys, rectangular keys, and Woodruff keys.)
FAQ: Where can I find a standard key size chart? (Standards organizations like ANSI and ISO publish key size charts.)
FAQ: How do I calculate the required key size? (Key size selection is based on shaft diameter and torque requirements. Consult relevant standards.)
FAQ: What materials are keys typically made of? (Common key materials include steel and stainless steel.)
FAQ: What are the consequences of using an incorrect key size? (An incorrect key size can lead to slippage, key failure, and shaft or hub damage.)
FAQ: How do I install a key? (Ensure proper alignment and a snug fit.)
FAQ: How do I troubleshoot key-related problems? (Inspect for wear, damage, and proper fit.)
In conclusion, understanding and applying the principles of standard key sizes for shafts is essential for ensuring reliable and efficient power transmission in a wide range of mechanical systems. From the simplest of machines to complex industrial equipment, the humble key plays a critical role in keeping things moving. By adhering to established standards, selecting appropriate materials, and employing best practices during installation and maintenance, you can maximize the lifespan of your equipment and avoid costly downtime. Proper key selection contributes to the overall efficiency and safety of your operations. Remember to consult relevant standards and seek expert advice when dealing with complex or demanding applications. The correct application of these principles will ultimately translate to smoother, more reliable, and cost-effective operation of your machinery.
Unlocking serenity exploring the nuances of sherwin williams aloof gray
The mystery of mona how old is mona simpson from the simpsons
Dr fong ping ching unveiling the enigma